Blog Archives
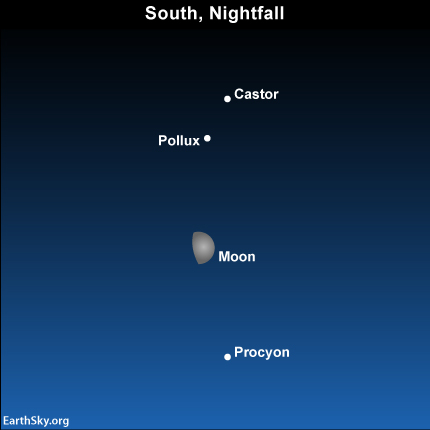
Moon between Procyon and Gemini
Hey, Do you see the moon tonite. Isn’t it beautiful? So what are these stars nearby? Or are they planets? The whole week it had been raining. But now, though the sporadic showers we can have a beautiful sky tonight.
Tonight at 11:00 p.m ( local Mauritian Time), in our sky the moon which is in its waxing gibbous phase, is between three stars. The star above the moon is Procyon. Procyon is the brightest star in the constellation Canis Minor (the small Dog). And below the moon we have two stars Castor and Pollux. These two stars are in the constellation Gemini (the Twins).
Towards the West, you can have a look at Sirius, the brightest star in our skies. Sirius is in the constellation Canis Major (the Big Dog). And towards North West you would have to raise your head to see Mars , a bright looking yellow star in the constellation Leo. Though as I said Mars looks like a star but is not. It’s a planet. So have a look before it starts raining cats and dogs again.
Did you know that in the Southern Hemisphere, the moon passes between the Gemini stars and Procyon once a month? And people living in the Northern Hemisphere will see the moon, Gemini stars, and Procyon in their southern evening sky. They’ll see the scene “upside down,” with Procyon shining below the moon, and Castor and Pollux above the moon?
You still don’t understand? Ok, just do the up-stand position in front of the night sky, you would get the “upside down” scene.
Asterisms : What? and List
Looking up and finding patterns in the stars is a pastime that’s as old as humanity. The constellations are rich with mythology that has been passed on for millennia.
The name for these unofficial constellations is “asterism.” Like constellations, asterisms have a long history. Some are regional, (this particular asterism list is from Germany) while others are universally recognized. Some are ancient, while others are more modern. If you enjoy stargazing, you may even have a few of your own personal asterisms. So go and be creative in the night sky and have fun.
If you are willing to find these asterisms, my advice would be to use Stellarium, if you still haven’t downloaded it, go grab it for free. you just have to type in the stars names in the Search field, for example: “delta Ori”,”epsilon Ori” and “zeta Ori”. And then you could be able to identify the asterism”the belt of Orion”. Pretty easy, huh!
Table of Asterisms:
Beehive |
Located in the constellation Cancer. It is an open star cluster, which is also called Praesepe or M44 and faintly visible to the naked eye.
|
Belt of Orion |
is being formed by the stars delta Ori, epsilon Ori and zeta Ori; in Latin Amerika it is called the “Three Marys”. |
Bier |
is being built by the four stars alpha UMa, beta UMa, gamma UMa and delta UMa.
|
Big Dipper |
most famous asterism. Formed by the following Stars of the Great Bear alpha UMa, beta UMa, gamma UMa, delta UMa, epsilon UMa, zeta UMa and eta UMa, it is often called “Wain” (Wagon) or “Charles’s Wain” because of its resemblance with it when the Dipper handle is thought to be the wagon tongue.
|
Bull of Poniatowski |
A T-shaped asterism just east of gamma Oph; it is formed by the stars 66 Oph, 67 Oph, 68 Oph and 70 Oph |
Circlet |
the western fish; the circlet is formed by gamma Psc, b Psc, theta Psc, iota Psc, 19 Psc, lambda Psc and kappa Psc. |
Coalsack |
Actually this is not a true asterism, but a dark patch on the Milky Way, in the constellation Crux. By the African Bushmen it was called “Old Bag”. |
Frederick’s Glory |
is formed by iota And, kappa And, lambda And and psi And |
Guardians of the Pole |
just beta UMi and gamma UMi |
Head of Cetus |
presented by alpha Cet, gamma Cet, xi_2 Cet, mu Cet and lambda Cet |
Heavenly G |
nine bright stars forming a G-shaped group. Seven of these stars are of 1st magnitude. In order they are: Aldebaran (alpha Tau), Capella (alpha Aur), Castor (alpha Gem), Pollux (beta Gem), Procyon (alpha CMi), Sirius (alpha CMa), Rigel (beta Ori), Bellatrix (gamma Ori) and Betelgeuse (alpha Ori) |
Hyades |
open cluster; V-shaped group superposed on alpha Tau, gamma Tau, delta Tau and epsilon Tau |
Hydra Head |
build by delta Hya, epsilon Hya, zeta Hya, eta Hya, rho Hya and sigma Hya |
Job’s Coffin |
formed by the four stars alpha Del, beta Del, gamma Del and delta Del |
Keystone |
is formed by the epsilon Her, zeta Her, eta Her and pi Her |
Kids |
are called epsilon Aur, zeta Aur and eta Aur |
Lozenge |
build by the four stars beta Dra, gamma Dra, xi Dra and nu Dra |
Milk Dipper |
The following five members of the constallation Sagittarius can be interpreted as an inverted dipper in the Milky Way: zeta Sgr, tau Sgr, sigma Sgr, phi Sgr and lambda Sgr. This asterism is also known as The Teapot. |
Northern Cross |
is formed by the leading stars of the constellation Cygnus: alpha Cyg, beta Cyg, gamma Cyg, delta Cyg and epsilon Cyg |
Northern Fly |
This is a small triangle over the rear of Aries |
Pleiades |
Located in the constellation Taurus. This open star cluster is one of the Messier objects, M45. It also known as Seven Sisters or, in Latin America the Seven Little Goats |
Segment of Perseus |
the stars eta Per, gamma Per, alpha Per, delta Per, epsilon Per and zeta Per forming an arc. |
Sickle |
formed by alpha Leo, eta Leo, gamma Leo, zeta Leo, mu Leo and epsilon Leo |
Square of Pegasus |
At the edges of that square you find alpa Peg, beta Peg, gamma Peg and alpha And |
Sword of Orion |
theta Ori and iota Ori; between them the famous Orion Nebula (M42) is located. |
Venus Mirror |
also on Orion; the belt stars (delta Ori, epsilon Ori and zeta Ori), the sword and eta Ori build up this asterism. The sword forms the handle of the diamond-shaped mirror. |
Y of Aquarius |
also called Water Jar; the Y is build by gamma Aqr, eta Aqr, pi Aqr and zeta Aqr |
Credits:
Related articles
- Constellations: Origins and Now (heavenswithlamps.wordpress.com)
The conjunction of Venus and Jupiter
What do you say about that?
Ahhh. That star…. it’s so bright. I see it almost nearly everyday from my room.
It’s so clear here….. I think this is the same star.
I was rather smiling at my friend at this point.
Etaaa …. You studied Physics your whole life and you don’t even know that this is not a star.
Ooh….Ohhh….Ohhh
This is planet Venus, the brighter one and the other is Jupiter.
I think this was too harsh for my friend who had just dropped by my house. Anyone looking at these planets would obviously say that these planets are stars. They shine so bright. As for Venus, wow, it is brighter than Sirius (the brightest star in our night sky) nowadays. But how to know if they are not stars. Stars shine and they shimmer in brightness (twinkle), but planets do shine but do not shimmer. Yeah if there is a wind then they would, but if it’s calm they won’t shimmer.
Looking towards the West Northwest as from the sunset until 8:00 pm, the conjunction of Venus and Jupiter would be easily seen. Venus and Jupiter would remain closer during the few days to come.
This News Bulletin just released by the The Astronomy And Nature Centre TV gives a good explanation coupled with a presentation on Stellarium.
If you want to get a quick idea of the conjunction in 90 seconds then listen to this podcast. If you ever fantasy tacking a picture of them just give me a shout.
Have your eyes up to the sky and you will appreciate the view.